Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasoundNuclear MedicineGeneral/Advanced ImagingImaging IT
Events

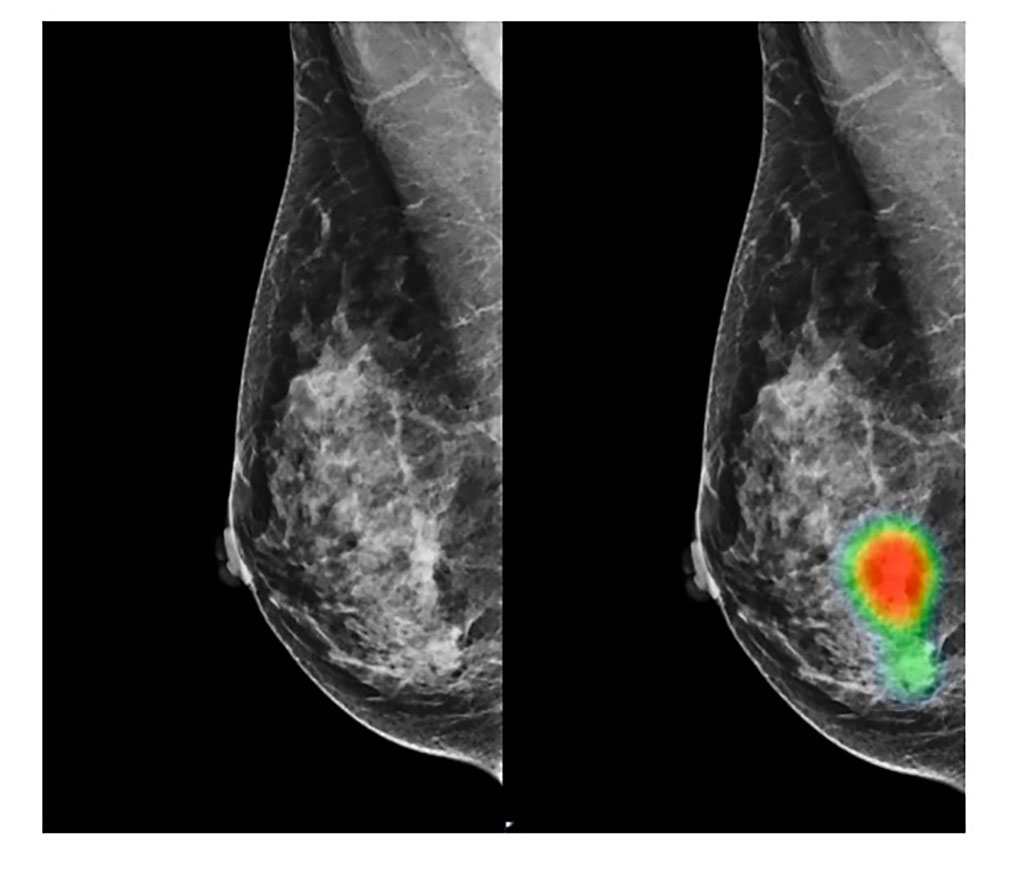
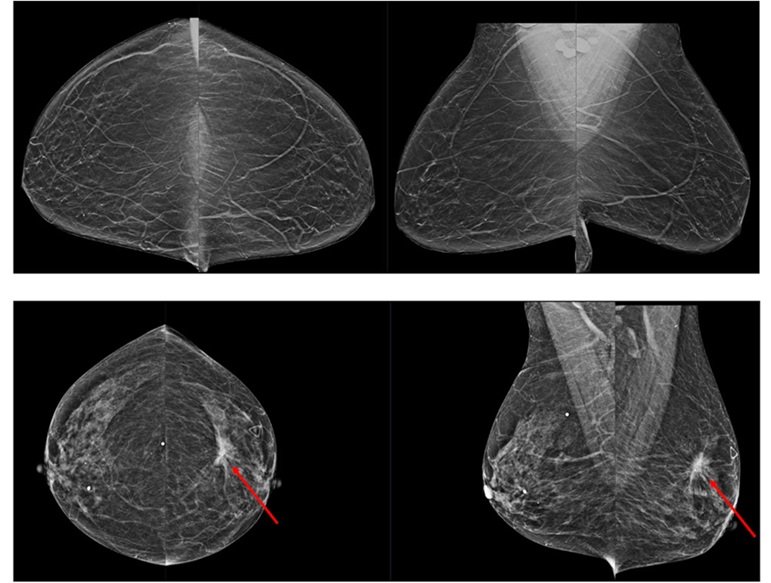
- AI Assistance Improves Breast-Cancer Screening by Reducing False Positives
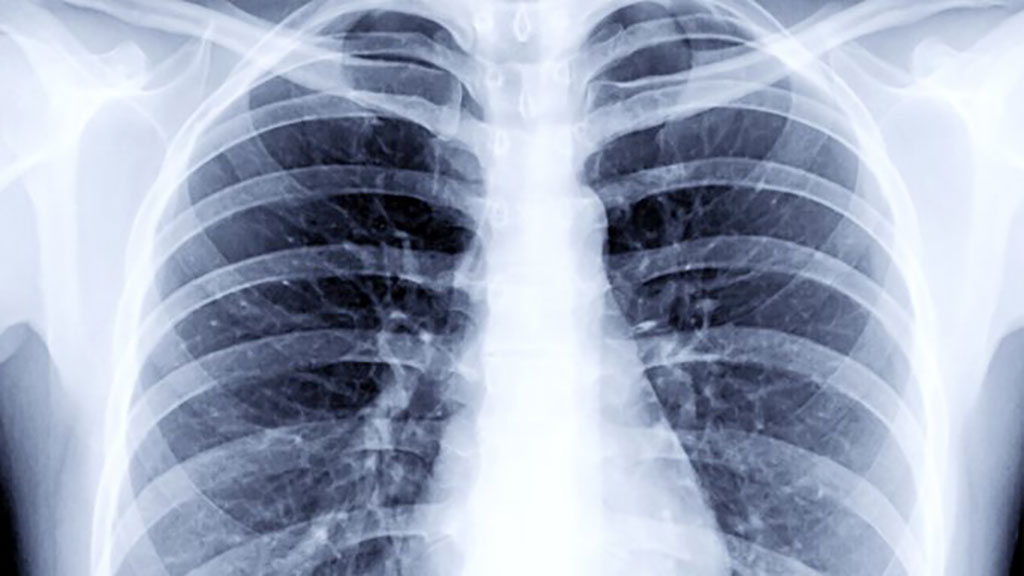
- AI Could Boost Clinical Adoption of Chest DDR
- 3D Mammography Almost Halves Breast Cancer Incidence between Two Screening Tests
- AI Model Predicts 5-Year Breast Cancer Risk from Mammograms
- Deep Learning Framework Detects Fractures in X-Ray Images With 99% Accuracy
- PET/MRI Improves Diagnostic Accuracy for Prostate Cancer Patients
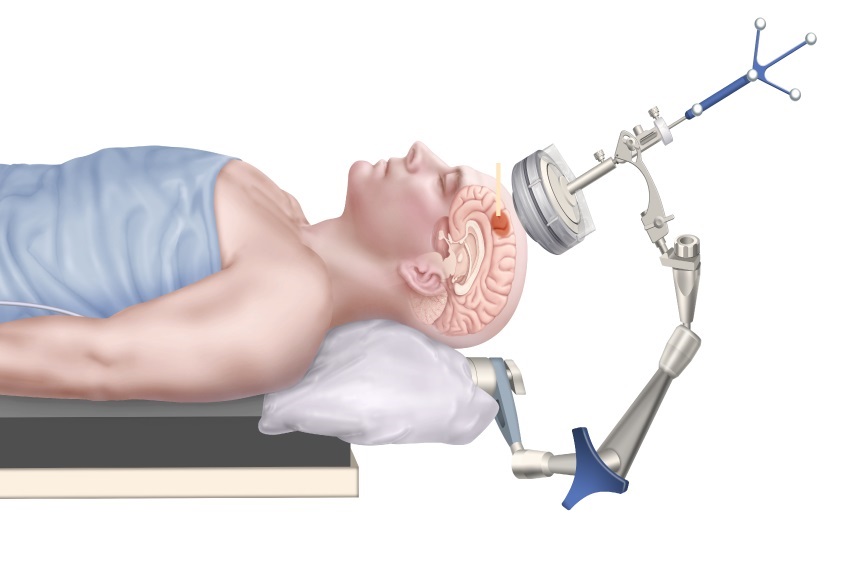
- Next Generation MR-Guided Focused Ultrasound Ushers In Future of Incisionless Neurosurgery
- Two-Part MRI Scan Detects Prostate Cancer More Quickly without Compromising Diagnostic Quality
- World’s Most Powerful MRI Machine Images Living Brain with Unrivaled Clarity
- New Whole-Body Imaging Technology Makes It Possible to View Inflammation on MRI Scan
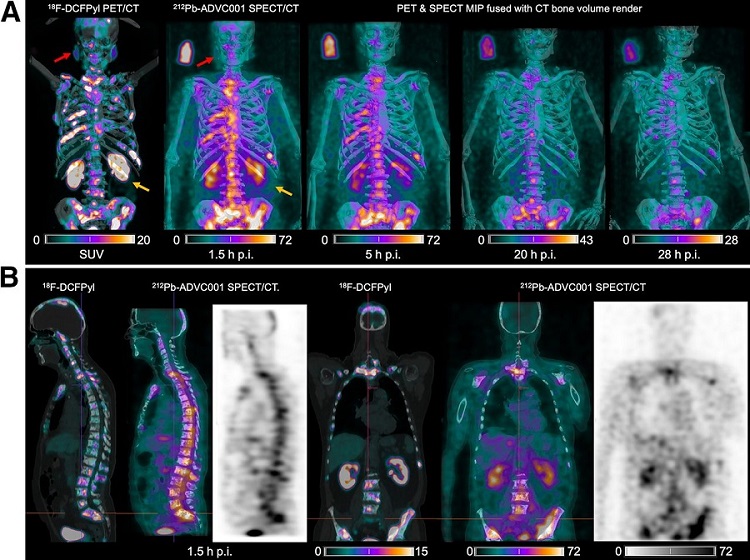
- New Radiotheranostic System Detects and Treats Ovarian Cancer Noninvasively
- AI System Automatically and Reliably Detects Cardiac Amyloidosis Using Scintigraphy Imaging
- Early 30-Minute Dynamic FDG-PET Acquisition Could Halve Lung Scan Times
- New Method for Triggering and Imaging Seizures to Help Guide Epilepsy Surgery
- Radioguided Surgery Accurately Detects and Removes Metastatic Lymph Nodes in Prostate Cancer Patients
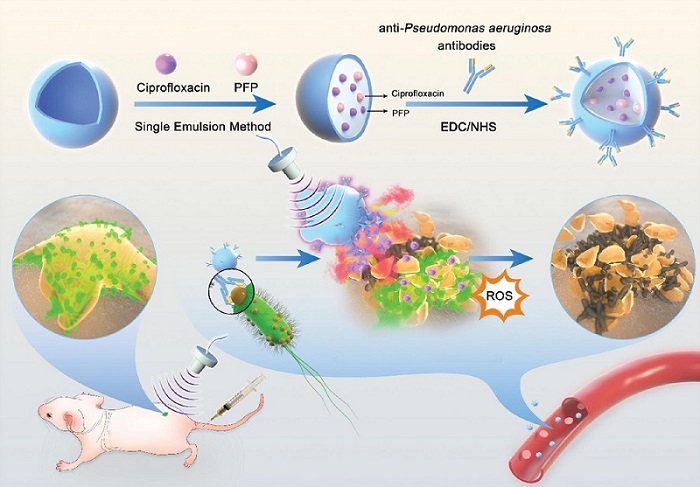
- Novel Ultrasound-Launched Targeted Nanoparticle Eliminates Biofilm and Bacterial Infection
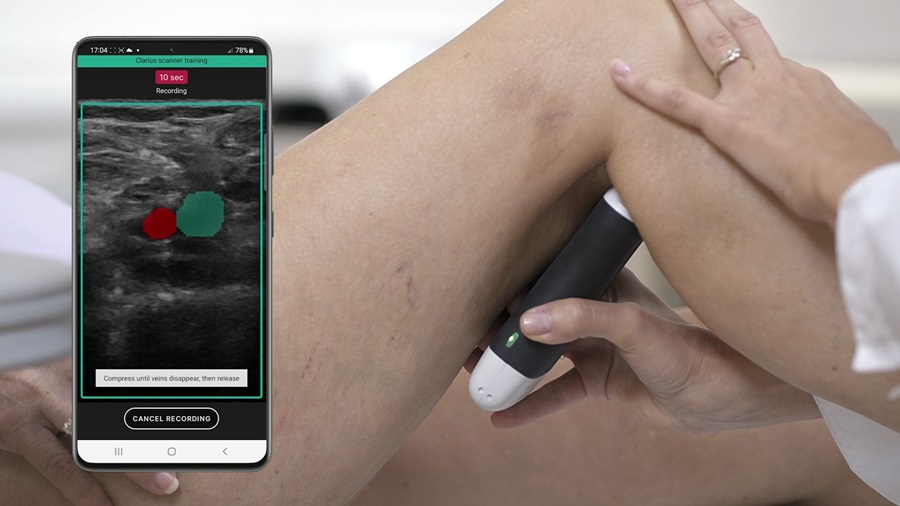
- AI-Guided Ultrasound System Enables Rapid Assessments of DVT
- Focused Ultrasound Technique Gets Quality Assurance Protocol
- AI-Guided Handheld Ultrasound System Helps Capture Diagnostic-Quality Cardiac Images
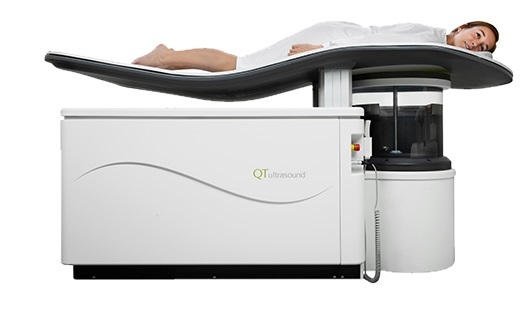
- Non-Invasive Ultrasound Imaging Device Diagnoses Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease
- CT Coronary Angiography Reduces Need for Invasive Tests to Diagnose Coronary Artery Disease
- Novel Blood Test Could Reduce Need for PET Imaging of Patients with Alzheimer’s
- CT-Based Deep Learning Algorithm Accurately Differentiates Benign From Malignant Vertebral Fractures
- Minimally Invasive Procedure Could Help Patients Avoid Thyroid Surgery
- Self-Driving Mobile C-Arm Reduces Imaging Time during Surgery
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Samsung and Bracco Enter Into New Diagnostic Ultrasound Technology Agreement
- IBA Acquires Radcal to Expand Medical Imaging Quality Assurance Offering
- International Societies Suggest Key Considerations for AI Radiology Tools
- Samsung's X-Ray Devices to Be Powered by Lunit AI Solutions for Advanced Chest Screening
- Canon Medical and Olympus Collaborate on Endoscopic Ultrasound Systems

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasoundNuclear MedicineGeneral/Advanced ImagingImaging IT
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
RadiographyMRIUltrasoundNuclear MedicineGeneral/Advanced ImagingImaging IT
Events
Advertise with Us


- AI Assistance Improves Breast-Cancer Screening by Reducing False Positives
- AI Could Boost Clinical Adoption of Chest DDR
- 3D Mammography Almost Halves Breast Cancer Incidence between Two Screening Tests
- AI Model Predicts 5-Year Breast Cancer Risk from Mammograms
- Deep Learning Framework Detects Fractures in X-Ray Images With 99% Accuracy
- PET/MRI Improves Diagnostic Accuracy for Prostate Cancer Patients
- Next Generation MR-Guided Focused Ultrasound Ushers In Future of Incisionless Neurosurgery
- Two-Part MRI Scan Detects Prostate Cancer More Quickly without Compromising Diagnostic Quality
- World’s Most Powerful MRI Machine Images Living Brain with Unrivaled Clarity
- New Whole-Body Imaging Technology Makes It Possible to View Inflammation on MRI Scan
- New Radiotheranostic System Detects and Treats Ovarian Cancer Noninvasively
- AI System Automatically and Reliably Detects Cardiac Amyloidosis Using Scintigraphy Imaging
- Early 30-Minute Dynamic FDG-PET Acquisition Could Halve Lung Scan Times
- New Method for Triggering and Imaging Seizures to Help Guide Epilepsy Surgery
- Radioguided Surgery Accurately Detects and Removes Metastatic Lymph Nodes in Prostate Cancer Patients
- Novel Ultrasound-Launched Targeted Nanoparticle Eliminates Biofilm and Bacterial Infection
- AI-Guided Ultrasound System Enables Rapid Assessments of DVT
- Focused Ultrasound Technique Gets Quality Assurance Protocol
- AI-Guided Handheld Ultrasound System Helps Capture Diagnostic-Quality Cardiac Images
- Non-Invasive Ultrasound Imaging Device Diagnoses Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease
- CT Coronary Angiography Reduces Need for Invasive Tests to Diagnose Coronary Artery Disease
- Novel Blood Test Could Reduce Need for PET Imaging of Patients with Alzheimer’s
- CT-Based Deep Learning Algorithm Accurately Differentiates Benign From Malignant Vertebral Fractures
- Minimally Invasive Procedure Could Help Patients Avoid Thyroid Surgery
- Self-Driving Mobile C-Arm Reduces Imaging Time during Surgery
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Samsung and Bracco Enter Into New Diagnostic Ultrasound Technology Agreement
- IBA Acquires Radcal to Expand Medical Imaging Quality Assurance Offering
- International Societies Suggest Key Considerations for AI Radiology Tools
- Samsung's X-Ray Devices to Be Powered by Lunit AI Solutions for Advanced Chest Screening
- Canon Medical and Olympus Collaborate on Endoscopic Ultrasound Systems


















.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)